Harness the Power of the Sun

Solar Powers World
“Your Ultimate Guide to Solar Powers Energy Solutions. Discover the latest in solar technology and learn how you can make a difference today.”
Explore the Benefits and Solutions of Solar Power
“Join the movement towards a greener, more sustainable future. Learn how solar energy can transform your home and business.”
Latest Article

Reliable 24v Inverter Pure Sine Wave Technology
Electricity powers most of the devices we rely on every day, so choosing the right inverter matters. A 24v inverter pure sine wave system converts battery direct current (DC) into clean alternating current (AC) like what you get…

Maximizing Solar Panel Efficiency for Sustainable Energy
The solar industry is advancing sustainable energy with high-performance modules such as the Maxeon 7. This solar panel is a leading example of residential solar panel efficiency, with manufacturer-reported lab efficiency around 24.9% and real-world…
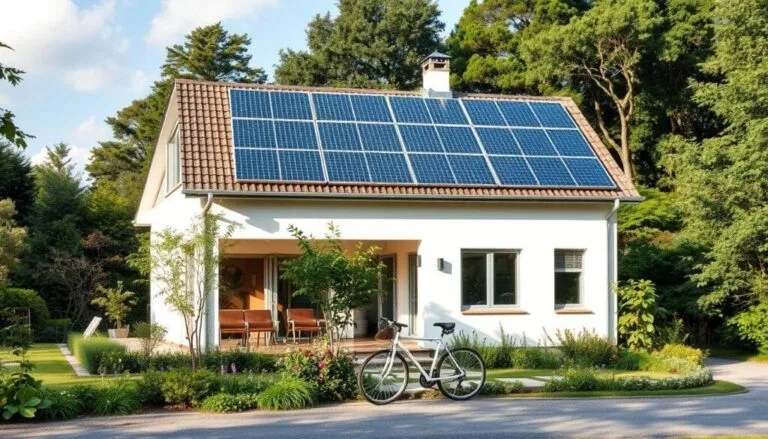

Discover Solar Rebates in Texas | Save on Solar Installations
Looking to harness the power of the sun and cut your energy bills? Solar Rebates Texas homeowners should know about can make switching to solar energy far more affordable. Texas ranks among the top states…
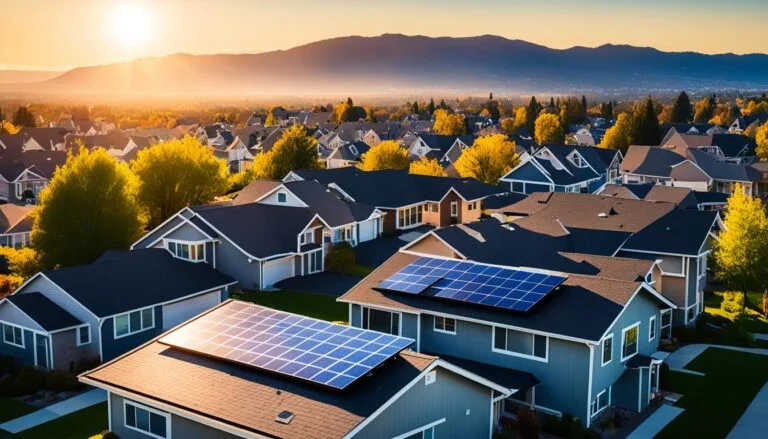

Solar Battery Cost: Factors, Incentives & Savings
More homeowners are turning to solar as an alternative energy source, so understanding solar battery cost and battery storage is essential. Solar batteries store extra energy from your solar panels for later use, giving your…
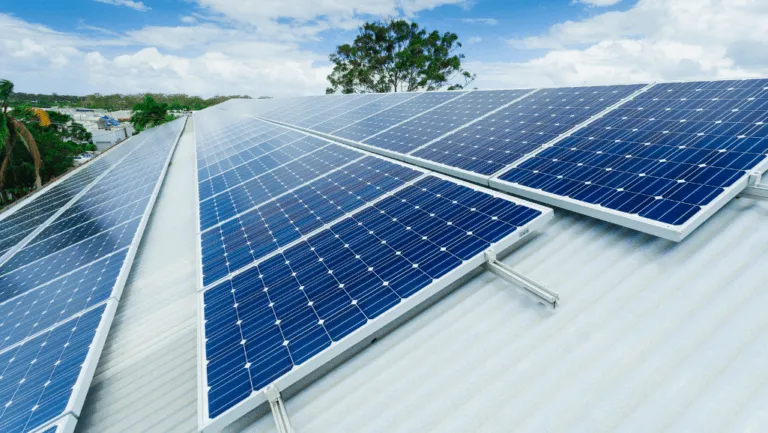

Boost Business with Commercial Solar Installation
Discover a future-proof investment that delivers more than energy savings. Commercial solar installation equips businesses with reliable sustainable power generation while strengthening a greener corporate identity. As utility rates rise in many regions, adopting solar offers businesses…
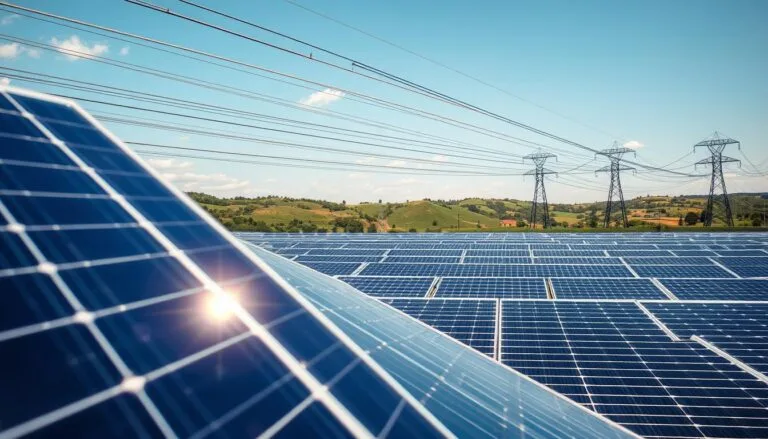

Solar Tax Credit: Save on Renewable Energy
Ready to harness the power of the sun? Solar tax credits make switching to clean energy more affordable by cutting the upfront cost of a home solar system. The federal solar investment tax credit (ITC)…
Expert insights and industry trends
Maximize Solar Energy
Part of the energy revolution
Utilize the
Repair
Empower Your Future with Solar Energy

Unlock the potential of solar powers and make a positive impact. Discover how renewable energy can revolutionize your lifestyle and reduce your carbon footprint.








Discover More
Discover the basics of solar energy. Learn how solar powers works, the different types of solar technologies, and the benefits of switching to solar energy for both residential and commercial use.
Contact with our professionals
Have questions about solar energy? Our experts are here to help. Whether you need advice on installation, maintenance, or the latest technologies, contact us for personalized support. Let’s harness the power of the sun together!












