Solar energy is changing the game in renewable energy. It’s a clean, sustainable option compared to fossil fuels. Solar energy can change how we make electricity and meet our energy needs. The solar power advantages include environmental benefits, cost savings, and energy independence.
In just an hour and a half, the sun’s energy can power the whole world for a year. This shows solar energy’s huge potential as a renewable source. By using solar radiation, we can cut down on fossil fuels and aim for a greener future.
Solar technology has improved a lot, making solar energy cheaper and more accessible. We see solar panels in homes and big solar farms. As more people and businesses use solar power, our planet and economy benefit, leading to a cleaner world.
Key Takeaways:
- Solar energy is a clean and renewable energy source that can significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
- The amount of sunlight reaching the Earth’s surface in a short period is sufficient to meet the world’s energy needs for an entire year.
- Solar technologies have become more advanced and cost-effective, making solar power accessible to a wider range of users.
- Embracing solar energy offers numerous benefits, including environmental protection, cost savings, and energy independence.
- The applications of solar energy are diverse, ranging from residential solar panels to large-scale solar farms.
Understanding Solar Energy
Solar energy is a clean and endless power source that uses the sun’s light and heat. It can change how we make electricity and cut down on fossil fuel use. Thanks to solar energy technologies, like photovoltaic cells, we can turn sunlight into energy we can use.
What is Solar Energy?
Solar energy is the sun’s light and heat that we can use to make electricity or heat. It’s a renewable energy that never runs out and can meet a lot of our energy needs. The sun’s energy comes to Earth as electromagnetic waves, giving us a clean and endless power source.
The Earth gets a huge amount of solar energy every day. In fact, it gets 200,000 times more energy than we use for electricity. This shows how much solar power can help meet our energy needs in the future.
How Does Solar Energy Work?
Solar energy technologies turn sunlight into electricity in different ways. Photovoltaic (PV) panels are the most common. They use many photovoltaic cells. When sunlight hits these cells, it makes electricity that can power homes and businesses.
Concentrating solar power (CSP) systems also capture solar energy. They use mirrors to focus sunlight onto a receiver. This receiver then turns the heat into electricity. CSP systems can even keep making electricity when it’s not sunny by using thermal storage.
Solar energy systems have gotten much better over time. Today’s photovoltaic cells can turn a lot of sunlight into electricity. Some are even over 20% efficient. This makes solar power more affordable and accessible for homes and businesses.
“Solar energy has the potential to play a significant role in meeting the world’s energy needs while reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change. With continued research and investment in solar energy technologies, we can unlock the full potential of this clean and renewable power source.”
The solar energy industry is growing fast. It’s clear that solar energy will be key to a sustainable future. Learning about solar energy helps us see its huge potential for powering our lives in a green way.
Solar Radiation Basics
Solar radiation is the key energy source for solar systems. The amount of solar energy available depends on location, time, season, landscape, and weather. A detailed solar resource assessment is vital for solar project success.
Solar radiation varies worldwide, with some areas getting more sunlight. The southwestern U.S. gets the most, making it great for solar projects. The U.S. Department of Energy says Earth gets enough solar energy in one hour to power the world for nearly a year.
To find out a site’s solar potential, solar assessments use tools and techniques. These include:
- Historical weather data
- Satellite imagery
- Geographic information systems (GIS)
- Ground-based measurements
By analyzing this data, experts can figure out solar levels and design solar systems.
“Understanding solar radiation basics is essential for harnessing the power of the sun and maximizing the benefits of solar energy technologies.”
The efficiency of solar tech, like PV cells and solar-thermal systems, depends on solar radiation. Over time, solar tech has gotten better, with PV modules now up to 20% efficient and some experimental cells almost 50% efficient.
| Solar Energy Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Total U.S. solar energy use increase (1984-2022) | 0.06 trillion Btu to 1,870 trillion Btu |
| U.S. solar electricity generation increase (1984-2022) | 5 million kWh to 204 billion kWh |
| Percentage of solar energy reflected back into space | 30% |
The solar energy industry is growing fast, with a 25% annual growth rate for the last decade. Knowing about solar radiation is key. By using site-specific assessments, we can make solar energy more effective and beneficial.
Photovoltaic Technology
Photovoltaic (PV) technology has changed how we use solar energy. It turns sunlight into electricity. At the core are photovoltaic cells, made from materials that absorb sunlight and create electricity.
These cells are put together to make solar panels. You can find them on rooftops, in solar farms, or in various products.
Photovoltaic Cells and Panels
Photovoltaic cells are the basic parts of solar panels. Most cells are made from silicon because it’s affordable and works well. But, scientists are looking into other materials to make them better and cheaper.
- Thin-film solar cells: These are light and flexible. They’re great for portable uses and even windows that make electricity.
- III-V solar cells: Made from certain elements, these cells are very efficient but cost more to make.
- Organic and hybrid solar cells: New technologies using organic and hybrid materials are being studied. They might make solar cells more efficient and affordable.
Solar Panel Efficiency and Performance
Solar panels have gotten much better over time. Their efficiency went from under 10% in the 1980s to about 15% by 2015. Now, the best panels can reach up to 25% efficiency.
Most panels today can turn about 11-15% of sunlight into electricity. Even on cloudy days, they can still make 30%-50% of their potential. On rainy days, they make about 10%-20%.
They also last up to 30 years, with the best performance in the first 25-30 years.
Advancements in Photovoltaic Technology
Research is always improving PV technology. This work aims to make solar panels more efficient, better performing, and cheaper. Some key advancements include:
| Advancement | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Bifacial solar panels | These panels can catch sunlight from both sides, boosting energy production | They can make up to 30% more electricity than regular panels |
| Perovskite solar cells | A new type of solar cell made from perovskite materials, offering high efficiency and low production costs | They could reach efficiency over 30% and cut solar energy costs |
| Solar tracking systems | Systems that let solar panels follow the sun, capturing more energy | They can increase energy production by 20-30% compared to fixed panels |
| Solar skin design | Customizable solar panel designs that look like other materials, like roof tiles or building facades | They make solar panels blend in with buildings, improving looks and use |
As PV technology keeps getting better, it will be key in the shift to renewable energy. With better efficiency, lower costs, and new uses, solar energy will help meet the world’s energy needs while protecting the environment.
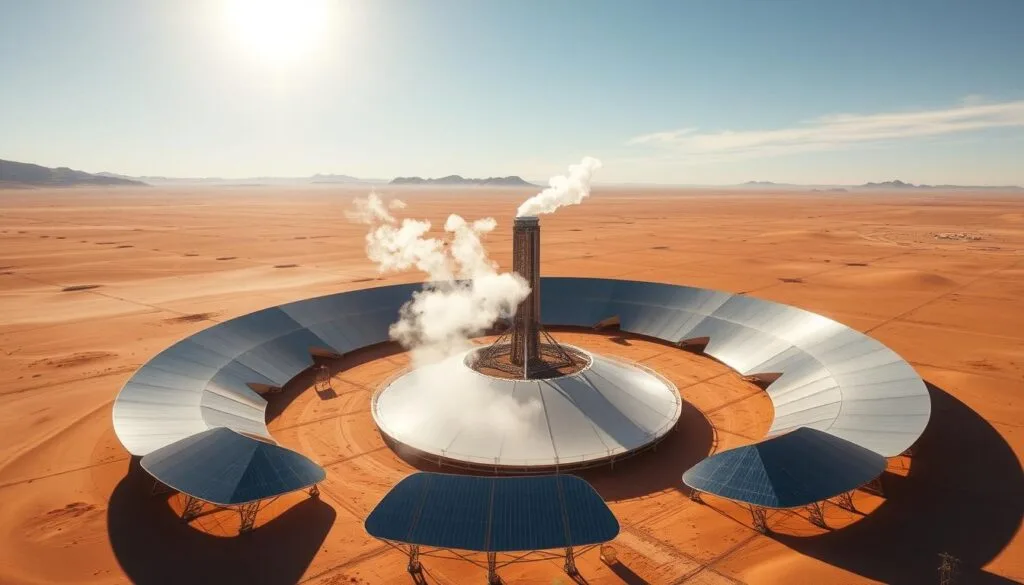
Concentrating Solar-Thermal Power
Concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP) is a new way to make electricity from the sun. It’s different from solar panels because it uses mirrors or lenses to focus sunlight. This heats a fluid that drives a turbine to make electricity.
This method lets CSP plants store thermal energy. This means they can still make power even when it’s dark.
Concentrating Solar-Thermal Power Systems
There are four main types of CSP systems. Each has its own design and benefits:
- Parabolic Trough Systems: These use long mirrors to focus sunlight on a tube. The tube heats oil, which makes steam to power a turbine.
- Linear Fresnel Reflectors: These use flat mirrors to focus sunlight on a fixed receiver. They are cheaper to make and maintain than parabolic troughs.
- Solar Power Towers: These use many mirrors to focus sunlight on a tower. The tower’s top has a receiver that heats molten salt to over 1,000°F. This heat makes steam to power a turbine.
- Dish-Engine Systems: These have a parabolic dish that reflects sunlight onto a receiver. The receiver has a heat engine that turns thermal energy into electricity.
Thermal Storage in Concentrating Solar-Thermal Power
CSP systems can store thermal energy. This lets them make electricity even when it’s dark. This is a big plus for renewable energy.
Right now, CSP plants can only store energy up to 565°C. But the U.S. Department of Energy wants to make it hotter, up to 720°C. This would make CSP systems more efficient and cheaper.
| CSP Plant | Location | Capacity | Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ivanpah Solar Power Facility | California, USA | 393 MW | Solar Power Tower |
| Crescent Dunes Solar Energy Project | Nevada, USA | 110 MW | Solar Power Tower with Energy Storage |
| Solana Generating Station | Arizona, USA | 280 MW | Parabolic Trough with Energy Storage |
The DOE wants CSP to be cheaper by 2030. They aim for 5 cents per kilowatt-hour for a plant that can run for 12 hours. For plants that run for less than six hours, they aim for 10 cents per kilowatt-hour.
To help reach these goals, the DOE is funding research. They are working on Solar Desalination, Generation 3 Concentrating Solar Power Systems, and Concentrating Optics for Lower Levelized Energy Costs.
As CSP technology gets better and costs go down, it could be a big part of the future of clean energy.
Solar Energy Integration
The world is moving towards a sustainable future. This means we need to use solar energy more in our homes, businesses, and electrical grid systems. We combine solar power with other energy sources. We also use smart grid technologies to manage energy better.
Integrating Solar Energy into Homes and Businesses
Using solar energy in homes and businesses helps us use less fossil fuel. It also cuts down our carbon footprint. Rooftop solar panels and small solar systems can make clean electricity. This can lower energy bills and make us more independent.
When adding solar energy, we must think about a few things:
- Roof orientation and shading
- Solar panel efficiency and performance
- Energy storage solutions, such as batteries
- Net metering policies and incentives
Solar Energy and Electrical Grid Systems
Adding solar energy to our grid systems is both a challenge and an opportunity. As solar power grows, our grid must adapt. It needs to keep the power stable and reliable.
Key aspects of solar integration with our grid include:
- Smart grid technologies for better energy management
- Energy storage to balance solar power’s ups and downs
- Upgrading grid infrastructure for two-way energy flow
- Creating policies to support solar energy
According to the International Energy Agency, solar PV is the fastest-growing electricity resource in the world. It makes up 2% of the global energy mix and 5% of the world’s electricity.
Distributed Energy Resources and Microgrids
Distributed energy resources (DERs) like solar panels, batteries, and electric cars are key to a decentralized energy system. Microgrids can work alone or with the main grid. They make our energy system more resilient.
Solar energy, DERs, and microgrids have many benefits. They include:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased energy resilience | Ability to keep power on during outages or emergencies |
| Reduced transmission losses | Generating electricity near where it’s used |
| Improved energy efficiency | Smart technologies optimize energy production and use |
| Greater community involvement | Local communities can control their energy future |
As solar and storage costs drop, more people can use solar-plus-storage solutions. Research and development are making these technologies better and cheaper. This is helping us move towards a sustainable and resilient energy future.
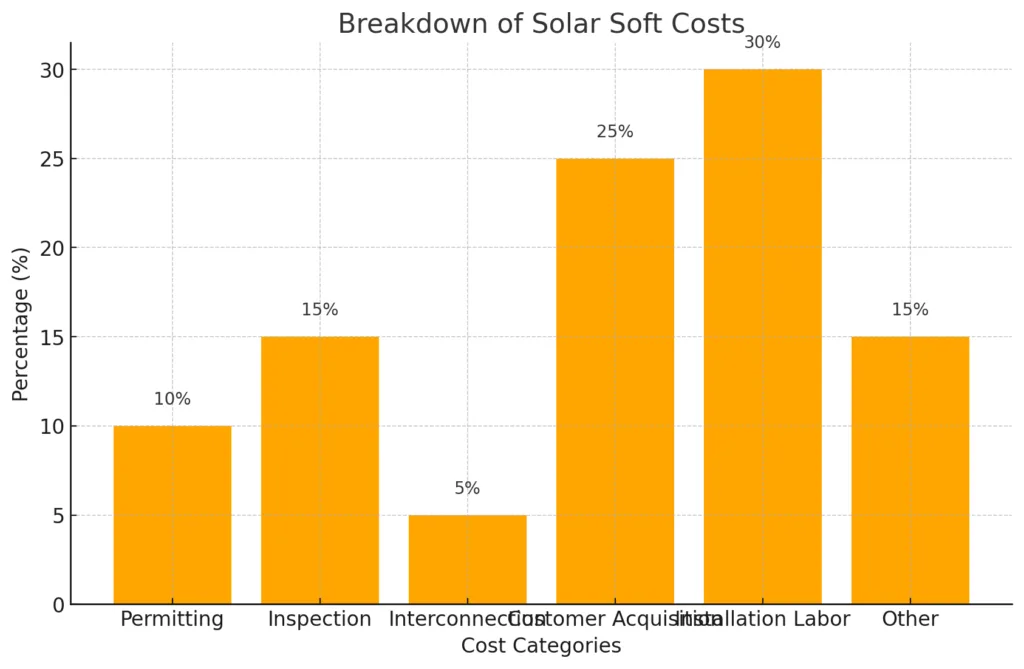
Soft Costs of Solar Energy
Hardware costs for solar systems have dropped a lot over the years. But, non-hardware expenses, or solar soft costs, still affect the total cost. These include things like solar permits, financing, and installation labor. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) says the cost of solar panels for homes fell by 64% from 2010 to 2020. Now, the average cost is between $3 to $4 per watt.
Even with lower hardware costs, soft costs still play a big role. In 2010, solar panels were two-thirds of the cost. But by the latest data, they are about 45% of the cost. By 2024, solar panels will be just 13% of the cost, with inverters and BOS equipment making up 33%.
Now, soft costs like labor and permits make up most of the cost. Labor is only 7% of the cost. But, customer acquisition, sales, and marketing efforts are 26%. Getting customers can cost around $1,000 per kW installed.
Companies like Solar.com aim to lower these costs. They connect installers directly with homeowners for better prices. There are also many financing options for solar panels, like cash purchases and loans.
| Cost Category | Percentage of Total Cost |
|---|---|
| Solar Panels | 45% |
| Inverters and BOS Equipment | 33% |
| Labor | 7% |
| Officework (including Customer Acquisition) | 26% |
The solar industry’s profit margin is over 20%, better than electric utilities. Despite challenges, the industry is growing fast. The number of solar workers in the US is expected to jump by 160% by 2020.
Lowering solar soft costs is key to making solar energy more affordable. Improving permits, financing, and installation can help reduce these costs. This will make solar power more accessible to everyone.
The solar industry is always innovating. Addressing soft costs is crucial to making solar power more affordable and widely used.
Benefits of Solar Energy
Solar energy brings many benefits, both for our planet and our wallets. It helps us use less fossil fuels, cuts down on harmful emissions, and fights climate change. Using solar energy makes our planet cleaner and more sustainable.
Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy
Solar energy is great for our environment. It lets us make electricity without using dirty fossil fuels. This means less pollution and less harm to our planet.
By choosing solar, we can make a big difference. We help fight climate change and keep our air clean.
Economic Benefits of Solar Energy
Solar energy also saves us money. Homeowners with solar panels pay less for electricity. They make their own power and don’t rely on the grid as much.
Installing solar panels can even increase your home’s value. It’s a smart choice for the future.
The solar industry also creates jobs and boosts the economy. As more people want solar, more jobs are made. Some places even let you sell solar energy for extra cash.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Home Value | Solar panels can increase a home’s resale value by up to $15,000 compared to neighboring homes without solar panels. |
| Long Lifespan | Solar panels have an average lifespan of 25 years, making them a long-lasting investment. |
| Income Potential | Some states offer Solar Renewable Energy Certificates (SRECs) that can be sold to earn money from solar energy production. |
| Cost Savings | Solar energy systems have the potential to reduce a home’s reliance on the grid and help save on electricity bills. |
Getting solar energy might seem expensive at first. But, there are ways to make it cheaper. Leasing options and government help can make solar energy more affordable.
There’s also a 30% tax credit for solar systems. This can help lower the cost even more.
“The environmental and economic benefits of solar energy are undeniable. By embracing this clean, renewable resource, we can create a brighter, more sustainable future for generations to come.” – Solar Energy Expert
Residential and Commercial Solar Applications
Solar energy is now more accessible for homes and businesses. Thanks to new tech and lower costs, more people are using solar power. This helps cut down energy bills, reduces carbon emissions, and supports a green future.
Residential Solar Systems
Residential solar panels are getting more popular. Homeowners can make their own electricity, cutting down on grid use and saving money. A typical 5-kilowatt system costs between $13,500 and $16,250.
The time it takes to pay back a solar system varies. It depends on where you live, how much energy you use, and any government incentives. On average, it’s 5-15 years. Plus, a 30% tax credit for solar systems is available until 2032.
Commercial Solar Projects
Businesses are seeing the benefits of solar too. Big solar projects can lower energy costs and show a company’s green commitment. These systems can power a lot of a business’s energy needs.
Going solar has more than just financial perks. It helps cut down on carbon emissions and supports the fight against climate change. Many companies are setting big goals for renewable energy, and solar projects help them meet these targets.
Community Solar Initiatives
Community solar projects are a great option for those without good roof space or money for solar. They let many people share the benefits of one solar system. This way, people can get solar energy without the costs or upkeep.
Community solar is open to more people, like renters and those in apartments. It helps grow renewable energy, supports a cleaner planet, and offers financial benefits without the initial costs or maintenance.
| Application | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Residential Solar Systems |
|
| Commercial Solar Projects |
|
| Community Solar Initiatives |
|
The future of solar energy is bright, with residential solar panels, commercial solar solutions, and community solar projects paving the way for a more sustainable and energy-independent world.
Solar Energy Industry and Market
The solar energy industry has grown a lot in recent years. This growth is due to lower costs, new technologies, and a bigger need for clean energy worldwide. As more countries and companies see the value of solar power, the market is set to keep growing.
Growth of the Solar Energy Industry
The solar industry has seen huge growth, with solar panel installations in the U.S. going up by 43% in 2019. This added 19.2 gigawatts of solar power, with 8 gigawatts in the last quarter of 2019. By 2020, the U.S. solar industry had 231,474 jobs, and this number is expected to go up with more federal support.
The cost of solar power has also dropped a lot. By December 2016, it was $1.65 per watt, making it cheaper than wind and fossil fuels. In 2016, a company in Dubai set a record by selling solar electricity for $0.029 per kilowatt-hour.
The U.S. has now over 2 million solar system installations and is on track to hit 4 million by 2023. The country’s solar capacity is over 135,700 megawatts, enough to power 24 million homes. The solar industry is expected to grow four times by 2030, thanks to falling costs and more demand for clean energy.
| Year | Solar Capacity (MW) | Homes Powered |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 40,000 | 7,200,000 |
| 2022 | 135,700 | 24,000,000 |
| 2023 (projected) | 210,000 | 36,000,000 |
Solar Energy Market Trends
Several trends are shaping the solar energy market. One key trend is the improvement in solar panel efficiency. In 2020, panels ranged from 20% to 23% efficient, a big jump from before. This improvement, along with lower costs, makes solar energy more affordable for homes and businesses.
Another trend is the integration of solar energy with storage systems. This allows users to store extra energy for when the sun isn’t shining. This makes solar power systems more reliable and appealing to consumers and businesses.
“The average cost per watt of solar panels in 2021 was $2.77, with quotes below $3.00 becoming increasingly common, making solar energy more accessible to a wider range of consumers.”
Floating solar farms are another exciting trend. These systems are installed on water, like lakes or oceans. They use less land, work better because of the cooling water, and can even help reduce water loss.
The solar industry is attracting more investments from governments and companies. Governments are offering incentives for solar power, and businesses see the financial and environmental benefits of solar projects.
- Solar energy installations accounted for 23.6 gigawatts in the U.S. in 2021, meeting the demand of 23.3 million American homes.
- Solar jobs in the U.S. have increased by 167% over the last decade, with over 255,000 workers in the solar industry.
- 22,000 square miles of solar panels could provide enough energy to power the entire United States.
Government Incentives and Policies
Governments worldwide are pushing for clean energy, especially solar power, to fight climate change. In the U.S., both federal and state governments have set up incentives and policies. These aim to encourage homeowners and businesses to use solar energy.
Federal and State Incentives for Solar Energy
The U.S. government offers a Residential Clean Energy Credit. It covers 30% of the cost of new, qualified clean energy for homes from 2022 to 2032. The percentage will decrease to 26% in 2033 and 22% in 2034. Qualified items include solar panels, water heaters, wind turbines, and more.
Many states also have their own solar energy incentives. These include grants, rebates, and performance-based incentives. These programs make solar energy more affordable and accessible. They help grow the solar industry at the state level.
From 2000 to 2020, renewable energy in the U.S. increased by 90%. It’s now the fastest-growing energy source. Growth is expected to continue at 2.4% annually for the next 30 years.
Solar Energy Policies and Regulations
Solar energy policies and solar regulations are also key. They create a supportive environment for the solar industry. Some important policies include:
- Net metering: 44 states and the District of Columbia have net metering policies. It lets solar system owners send excess electricity back to the grid and get credit.
- Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS): Some states require a certain percentage of electric power to come from renewables, like solar.
- Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs): Companies use RECs to meet emission reduction targets or goals.
- Green Power Programs: States offer programs for consumers to choose electricity from renewable sources.
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and federal agencies fund research for renewable energy. DOE’s national laboratories help advance solar technology.
| State | Percentage of Total U.S. Solar Energy Generation |
|---|---|
| California | 27.5% |
| Texas | 11% |
As the U.S. invests in cleaner energy, incentives and policies will keep driving solar energy adoption. This will help reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Facts About Solar Energy
Solar energy is changing how we power our homes, businesses, and communities. It’s a clean, sustainable, and affordable solution to reduce carbon emissions and fight climate change. We’ll explore interesting solar energy facts, look at solar power statistics, and clear up myths about this technology.
Impressive Solar Energy Statistics
The growth of solar energy is remarkable. Since 2000, the amount of solar power installed worldwide has grown by over 300 times. In the U.S., solar installations have jumped by more than 23 times in eight years, from 1.2 GW in 2008 to 27.4 GW by 2015.
The U.S. is now the third-largest solar market, with projections to soon be second. Solar panels are set to provide 25% of the world’s electricity by 2050. In the UK, over 1.4 million homes use solar panels, showing the power of the sun.
| Solar Energy Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Solar power installed globally since 2000 | Increased by over 300 times |
| Solar power installations in the U.S. (2008-2015) | Increased from 1.2 GW to 27.4 GW |
| Projected share of world’s electricity from solar panels by 2050 | 25% |
| Homes in the UK with solar panels | More than 1.4 million |
| Global solar panel production in 2022 | Around 379 GW |
Surprising Facts About Solar Power
Solar energy is incredibly abundant, with 173,000 terawatts hitting Earth daily. This is more than 10,000 times the world’s total energy use. The solar energy hitting Earth in a year is 29,000 times more than the U.S. consumes annually.
Solar panels can handle high temperatures, from 65°C to 85°C. This means they work well even in hot climates. Plus, solar power systems produce little to no emissions or waste, making them eco-friendly.
Debunking Common Solar Energy Myths
Many people think solar panels don’t work in cold or cloudy weather. But this is a myth. Solar panels can still generate electricity, even when it’s not sunny, though not as efficiently.
Another myth is that solar energy is too expensive. While it’s true that initial costs can be high, prices have been dropping. Government incentives and policies help make solar energy more affordable for everyone.
The sun provides more than enough energy to meet the whole world’s energy needs, and unlike fossil fuels, it won’t run out anytime soon. As a renewable energy source, solar energy is an important part of our clean energy future. – National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL)
Conclusion
The future of solar energy looks bright. It could change how we make and use power. With better tech and lower costs, solar energy is set to play a big role in our shift to renewable energy.
Solar power can give us more energy in one hour than we use in a whole year. This shows its huge potential. It’s a clean and green way to power our lives.
Solar panels can run cars, boats, homes, and businesses. They offer many uses. Plus, solar energy can create jobs and save money on energy bills.
But, solar power isn’t always available, and we need better ways to store it. Yet, scientists and companies are working hard to solve these problems. With everyone’s help, solar energy will grow, leading to a cleaner future.
By using the sun’s power and investing in solar tech, we can make our world more sustainable. This will help us transition to renewable energy successfully.