Solar energy conversion shows how we use the sun’s power. In just an hour and a half, the sun’s rays could give us enough energy for a year. Solar technology is key, turning sunlight into electric power. It does this using photovoltaic (PV) and concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP) systems.
So, how does solar energy work? PV panels catch sunlight to make electricity. CSP systems use mirrors to focus the sun’s energy, creating heat. This heat can be turned into electricity right away or saved for later. These technologies blend traditional and renewable energy, fitting into our daily lives and the power grid.
Key Takeaways
- how is the solar energy generated.
- Understanding solar energy generation is crucial for using the sun’s power.
- Photovoltaic and concentrating solar-thermal power systems are key to solar energy conversion.
- Soft costs often make up a big part of the cost of solar systems.
- Solar energy fits into homes, businesses, and the power grid.
- More solar technology means cleaner energy, more jobs, and economic growth.
- The U.S. and other countries support solar power with research and infrastructure.
The Sun’s Power: Understanding Solar Radiation
At the core of the solar energy process, solar radiation is key. It sends out energy that can turn into heat and electricity. This energy supports our planet’s ecosystems and powers sustainable energy technologies.
What is Solar Radiation?
Solar radiation includes the energy the Sun sends out. This energy has visible and invisible parts, like light, infrared, and ultraviolet rays. It’s what makes photosynthesis happen and is vital for life on Earth. It also fuels solar energy technologies.
How Does Solar Radiation Vary Across the Globe?
The amount of solar radiation changes a lot, depending on where you are on Earth. It’s affected by your location, the time of day, the season, and the weather. Knowing this helps us make the most of solar energy.
Places near the equator get more solar radiation, making them great for solar energy. But areas with lots of clouds or are far north or south get less, which can be a challenge.
To use solar radiation well, we need to understand it deeply. Things like the atmosphere and clouds can change how much energy solar panels get. Knowing this helps us improve sustainable energy and move towards a cleaner future.
How Is the Solar Energy Generated: Photovoltaic Systems Explained

Photovoltaic systems are key to the growth of solar panels energy production. They use the photovoltaic effect to turn sunlight into electricity. This effect was discovered in 1839. Sunlight hits PV cells, creating electrical charges and a current.
Since its start, solar panel efficiency has been vital. It has improved from small devices to big power stations. This has made solar energy more useful.
Technology in photovoltaic systems has boosted solar panel efficiency. PV panels used to be less than 10% efficient in the 1980s. Now, they’re about 15% efficient, and the best ones can reach 25%.
This means they produce more energy. For example, electricity from solar plants grew from 6 million kilowatthours in 2004 to 162 billion kilowatthours in 2023. Rooftop PV systems also increased, from 11 billion kilowatthours in 2014 to 74 billion kilowatthours in 2023.
| Year | Utility-Scale Generation (billion kWh) | Small-Scale Generation (billion kWh) | Panel Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 0.006 | — | |
| 2014 | — | 11 | ~15 |
| 2023 | 162 | 74 | ~25 |
Some things affect how well photovoltaic systems work. Temperature and dirt can lower efficiency. A panel might lose 0.5% efficiency for every degree Celsius over 25°C. Dirt can cut output by about 5%.
But, new technologies and better installation methods are making these systems better. They’re making solar panels energy production a good alternative to traditional energy sources.
Components of Solar Panels and Their Function
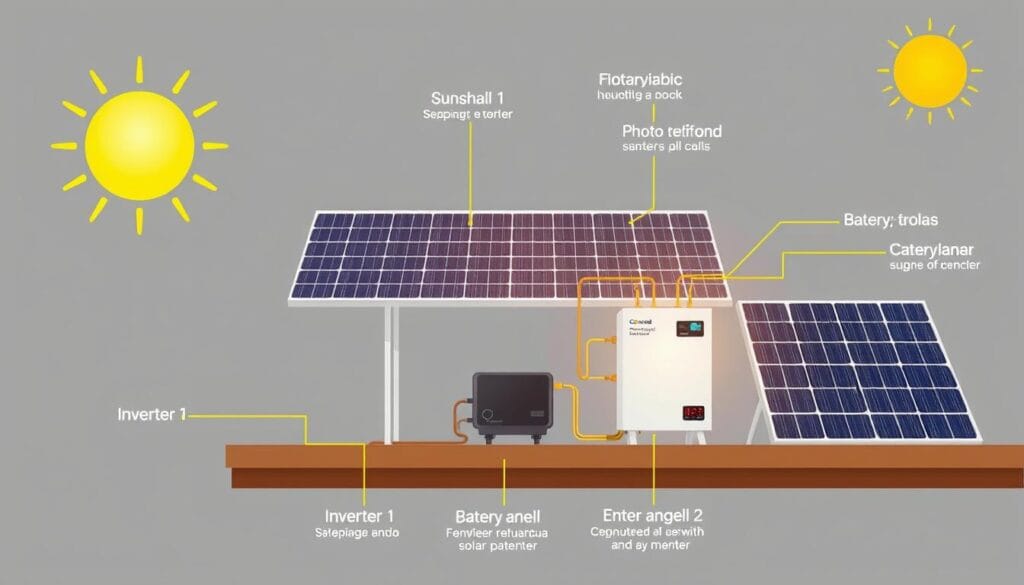
Solar panels are a blend of technology and engineering. They turn sunlight into electricity efficiently. As we seek sustainable energy, knowing how solar panels work is key. Solar technology has improved, making these parts work together well.
Understanding Photovoltaic Cells
Photovoltaic (PV) cells are crucial in solar technology. They’re made from silicon, which is great for its properties. These cells catch sunlight and turn it into electricity. There are two main types: monocrystalline and polycrystalline.
Monocrystalline cells work better and look sleek but cost more. Polycrystalline cells are cheaper but not as efficient. Thanks to new tech, PV cells are getting better and more reliable.
They have layers that help absorb and convert sunlight well. The material and design of PV cells affect how well solar panels work and their cost.
Electricity Generation via Solar Panels
Solar panels work by using photons to free electrons from atoms, creating electricity. This is the main idea behind solar power. The sunlight hits PV cells, starting the flow of electrons and making DC electricity.
This DC electricity then turns into AC electricity with an inverter. This makes it ready for use at home or in businesses. The performance of solar panels also depends on inverters and storage systems.
String and microinverters are important for converting electricity well. Adding Energy Storage Systems (ESS) can store extra electricity for later. This means you always have power.
| Component | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Silicon Cells | Semiconductor material for capturing sunlight | Monocrystalline/Polycrystalline |
| Metal Frame | Provides structure and durability | Aluminum |
| Glass Casing | Protects silicon cells and enhances efficiency | Anti-reflective |
| Inverter | Converts DC to usable AC electricity | String/Microinverters |
| ESS | Stores excess power for later use | Solar Batteries |
Understanding these parts is key to knowing how solar panels work. They all work together to make solar energy efficient. As solar tech gets better, these parts will help us use the sun’s energy better, leading to a greener future.
Concentrating Solar-Thermal Power (CSP) Technologies
Concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP) is a key way to make solar power. It uses mirrors to focus sunlight into intense heat. This process turns heat into electricity or stores it for later use. It’s great for making a lot of power.
The Role of Mirrors and Concentrated Sunlight
Mirrors are key in CSP technology. They come in trough systems, power towers, or dish/engine systems. These mirrors focus sunlight onto a point or line.
Trough systems heat oil in pipes to 750°F. Power towers can heat molten salt to 1,050°F. This heat makes steam turbines or heat engines, which generate electricity.
Thermal Storage in CSP Systems
CSP systems can store heat for later use. They save excess heat in molten salts during the day. This heat can make electricity when the sun isn’t out.
This makes solar energy more reliable and helps the power grid during busy times.
There’s a lot of research into making CSP better. Groups like Sandia National Laboratories and the Solar Energy Technologies Office are working on new parts. They aim to make CSP more efficient and cheaper.
New projects show how well CSP works. For example, Hyperlight Energy used solar-thermal power at a cheese factory in California. New tech like supercritical carbon dioxide power cycles could make CSP even cheaper.
The Solar Energy Development PEIS looks at how CSP affects the environment. It makes sure solar tech grows in a way that’s good for the planet. The future of CSP looks bright, with more energy efficiency and green solutions.
Integration of Solar Power in the Electrical Grid

Adding solar power to the electrical grid is key for the solar energy industry’s growth. It involves both technical and regulatory aspects to blend smoothly with the existing grid. As renewable energy grows, knowing how solar energy works with the grid is vital.
Challenges and Solutions in Solar Energy Integration
Solar power’s main challenge is its unpredictable nature, changing with daylight and weather. This can cause issues with grid stability. To fix this, energy storage systems like batteries are vital. They store extra energy for when the sun isn’t shining, keeping the energy flow steady.
Integrating solar power also requires advanced grid management systems. These systems can handle the power from many solar sources. Smart grid technologies help manage power supply and demand in real-time. Inverters are also key, changing solar panels’ DC power to AC, making it work with the current grid.
Grid Services and Energy Management
Solar energy helps balance the grid by adjusting power supply with demand. Net metering lets homeowners send extra solar power back to the grid, reducing their energy bills. This shows the economic and efficiency gains of solar in energy systems.
Time-based rate plans encourage using energy when solar power is plentiful. This helps balance energy use and reduces strain on the grid. Solar energy also cuts down on maintenance and upgrade costs for utilities, making the grid more efficient.
The solar industry is expanding, especially in sunny areas like Hurst, TX, Keller, TX, and Southlake, TX. This growth will improve both local and large-scale electrical systems. With these advances, a strong, sustainable grid that uses renewable energy is closer, paving the way for a greener energy future.
Soft Costs: The Non-Hardware Side of Solar Energy
The move to sustainable energy has made us realize how big a deal soft costs of solar energy are. These costs are not about hardware but about things like permits, setup, and running costs. They make up a big part of the total cost, especially for rooftop solar setups. This affects how affordable and accessible solar power is.
For businesses and homeowners, knowing what these costs are is key. High soft costs come from things like solar workforce development, rules, and how well companies get customers. Even with hardware costs dropping by up to 160% since 2010, soft costs still make up to 64% of solar system costs.
Efforts to make the permitting process smoother and cut down on waste have started. Programs that give tools and knowledge help lower costs. Better software for companies also helps manage portfolios and sales, reducing soft costs. The benefits of these improvements are big, but we also need to teach professionals like real estate and fire safety about solar installations.
Local solutions like community solar and local funding for solar projects are helping make solar energy cheaper for more people, especially in areas that need it most. These efforts show that cutting soft costs is about more than just saving money. It’s also about getting more people to use solar energy.
| Solar Cost Factor | Percentage of Total Cost | Impact on Solar Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| Permitting and Installation | 30% | High |
| Operational Expenses | 20% | Medium |
| Solar Workforce Training | 14% | High |
| Customer Acquisition | 36% | Very High |
The solar industry needs to keep innovating, not just in tech but also in managing soft costs. Cutting down these costs is crucial for staying competitive and getting more people to use solar energy.
The Various Applications of Solar Energy
Solar energy uses many technologies, from small home systems to big solar farms. It’s a key renewable energy source. It helps many sectors be more sustainable and efficient.
Residential and Commercial Uses
Home solar setups help power lights, heat water, and run appliances. They use photovoltaic panels and solar water heaters. This cuts down on traditional power use and lowers bills.
For businesses, solar tech meets bigger needs like in hotels and schools. It supports heavy loads like heating and lighting. Companies save on energy costs and help the environment.
Large Scale Solar Farms and Their Impact
Solar farms make a lot of electricity, helping us move away from fossil fuels. They cover huge areas with solar panels, sometimes on water. This is called floating solar farms.
These big projects power many homes and businesses. They cut down on harmful emissions and make energy more secure. They also use land wisely and create jobs in renewable energy.
Solar farms work well with other energy sources, like wind or hydroelectric power. This shows a strong future for energy networks.
From small home setups to big solar farms, solar energy is growing. It’s used in many places around the world.
Technological Advances and Solar Panel Efficiency
The need for sustainable energy is growing fast. Improving solar panel efficiency is crucial. New advances in photovoltaic cell technology and solar technology advancements are making solar energy more efficient.
Developments in Solar Technology
New tech has made solar panels work better. Researchers like Adrienne Stiff-Roberts at Duke University are finding new ways to use solar energy. They’re working on materials that mix organic and inorganic parts, making solar panels more efficient.
This work is key because it could make solar power cheaper and use less land. Advances in solar technology mean we could get more energy from the same amount of sunlight.
Improving Solar Energy Conversion Efficiency
Solar panels have gotten much better over time. They used to turn just 6% of sunlight into power, but now they can turn about 22% to 23%. A special solar cell made by scientists at NREL even reached 47.1% efficiency under certain conditions.
This shows we could make solar power even better. It also means solar energy could get cheaper. Swanson’s Law says the price of solar modules should drop by 20% every time the amount of solar power made doubles.
Researchers are now working on ways to reduce light reflection and manage heat. This will help solar panels work better in hot weather.
By combining better materials, new tech, and smart manufacturing, we can make solar energy a big part of the world’s power. This will help us use energy in a more sustainable way.
Conclusion
The journey of solar energy from the sun to Earth shows our creativity. Just one hour of sunlight can meet our energy needs for a year. This shows solar power’s big promise for a green future.
In the solar energy industry, research drives progress. It’s making solar energy cheaper and more efficient. Experts believe solar energy will soon be a key energy source thanks to these advances.
Researchers are always finding new ways to make solar panels better and cheaper. They’re also working on using more land for solar projects. Governments are helping by offering tax breaks and subsidies for solar projects.
Solar power is versatile, powering cars, lights, and devices. It helps reduce pollution and can lower our energy bills. California is a leader in using solar power at home, showing its benefits.
But, there are challenges like the need for more sunlight, finding land, and the environmental impact of making panels. These issues need more research and support. Costs are important too, making sure solar energy is worth it.
The solar industry and society are working together for a clean energy future. With everyone’s effort, solar energy could become a key part of our energy mix.






















